Measuring single-cell density
William H. Grover, Andrea K. Bryan, Monica Diez-Silva, Subra Suresh, John M. Higgins, and Scott R. Manalis, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 108 (27), 10992-10996 (2011). PDF
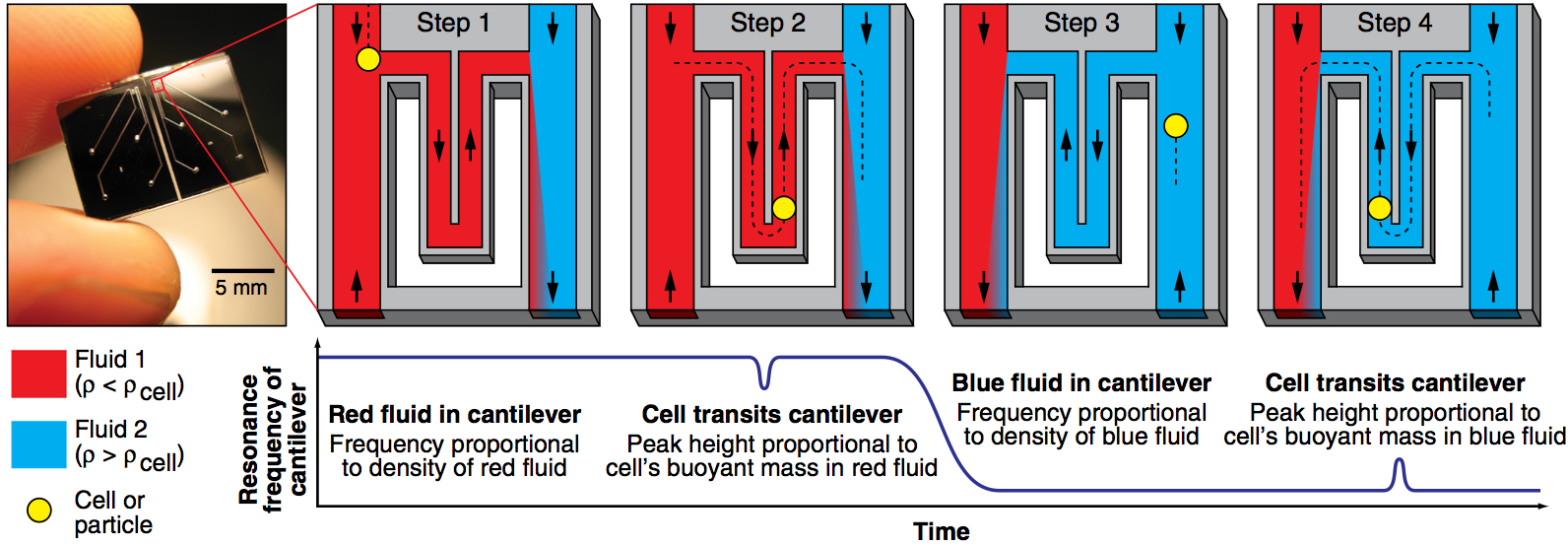
We have used a microfluidic mass sensor to measure the density of single living cells. By weighing each cell in two fluids of different densities, our technique measures the single-cell mass, volume, and density of approximately 500 cells per hour with a density precision of 0.001 g/mL. We observe that the intrinsic cell-to-cell variation in density is nearly 100-fold smaller than the mass or volume variation. As a result, we can measure changes in cell density indicative of cellular processes that would be otherwise undetectable by mass or volume measurements. Here we demonstrate this with four examples: identifying P. falciparum malaria-infected erythrocytes in a culture, distinguishing transfused blood cells from a patient’s own blood, identifying irreversibly-sickled cells in a sickle cell patient, and identifying leukemia cells in the early stages of responding to a drug treatment. These demonstrations suggest that the ability to measure single cell density will provide valuable insights into cell state for a wide range of biological processes.