Disintegration Fingerprinting preprint on medRxiv
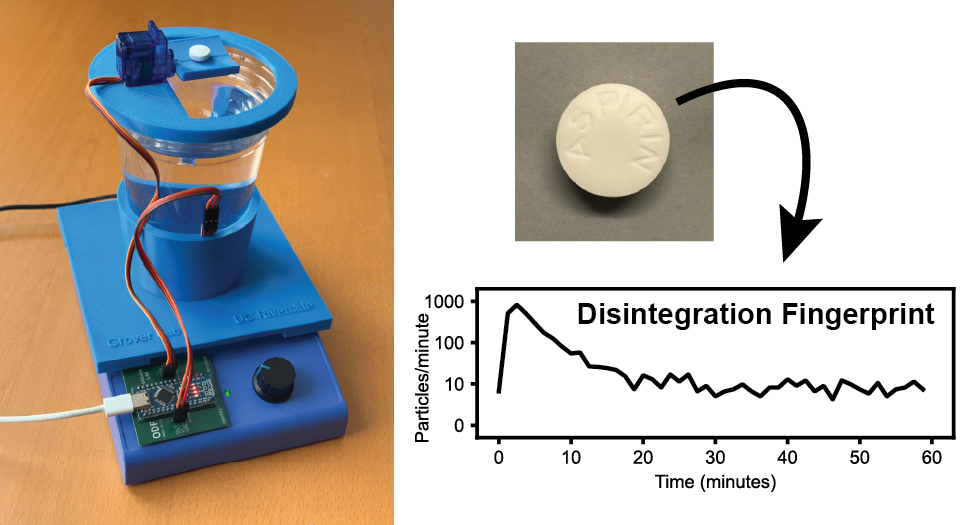
Our latest low-cost technique for identifying counterfeit medicines is the subject of a new preprint on medRxiv.
Disintegration fingerprinting uses a water-filled transparent plastic cup atop a conventional magnetic stirrer. An inexpensive sensor mounted on the outside of the cup shines infrared light into the cup and measures the amount of light that is reflected back to the sensor. When a pill is added to the stirred water, the pill begins to disintegrate into particles that swirl around inside the cup. Whenever one of these particles passes near the infrared sensor, the particle reflects additional light back to the sensor and creates a millisecond-duration peak in a plot of sensor output vs. time. The number of particles in the water changes over time as the particles continue to disintegrate and (in some cases) eventually dissolve away. By plotting the number of particles detected vs. time, we create a Disintegration Fingerprint that can be used to identify the drug product. In a proof-of-concept study, we used DF to analyze 96 pills from 32 different drug products (including antibiotics, opioid and non-opioid analgesics, antidepressants, anti-inflammatories, antiemetics, antihistamines, decongestants, muscle relaxants, expectorants, sleep aids, cold medicines, antacids, hormonal birth control, and dietary supplements, as well as a simulated falsified drug product). We found that DF correctly identified 90% of these pills, and the technique can even distinguish name-brand and generic versions of the same drug. By providing a fast (60-minute), inexpensive ($33 USD), and easy-to-use tool for identifying substandard and falsified medicines, Disintegration Fingerprinting can play an important role in the fight against fake drugs.